Junction table
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article does not cite any references or sources. (December 2009) |
In database management systems following the relational model, a junction table is a database table that contains common fields from two or more other database tables within the same database. It is on the many side of a one-to-many relationship with each of the other tables. Junction tables are known under many names, among them cross-reference table, bridge table,join table, map table, intersection table, linking table, many-to-many resolver, link table, pairing table, pivot table, transition table, or association table.
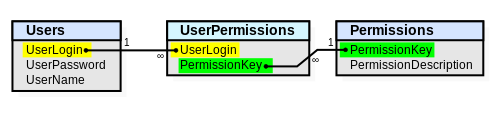
Junction tables are employed when dealing with many-to-many relationships in a database. A practical use of a junction table would be to assign permissions to users. There can be multiple users, and each user can be assigned 0 or more permissions.
CREATE TABLE Users ( UserLogin VARCHAR(50) PRIMARY KEY, UserPassword VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, UserName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL ) CREATE TABLE Permissions ( PermissionKey VARCHAR(50) PRIMARY KEY, PermissionDescription VARCHAR(500) NOT NULL ) -- This is the junction table. CREATE TABLE UserPermissions ( UserLogin VARCHAR(50) REFERENCES Users (UserLogin), PermissionKey VARCHAR(50) REFERENCES Permissions (PermissionKey), PRIMARY KEY (UserLogin, PermissionKey) )
Using junction tables[edit]
A SELECT-statement on a junction table usually involves joining the main table with the junction table:
SELECT * FROM Users JOIN UserPermissions USING (UserLogin);
This will return a list of all users and their permissions.
Inserting into a junction table involves two steps: first inserting into the main table (for example, a new User), then updating the junction table.
-- Creating a new User INSERT INTO Users (UserLogin, UserPassword, UserName) VALUES ('SomeUser', 'SecretPassword', 'UserName'); -- Creating a new Permission INSERT INTO Permissions (PermissionKey, PermissionDescription) VALUES ('TheKey', 'A key used for several permissions'); -- Finally, updating the junction INSERT INTO UserPermissions (UserLogin, PermissionKey) VALUES ('SomeUser', 'TheKey');
Using foreign keys, the database will automatically dereference the values of the UserPermissions table to their own table.
No comments:
Post a Comment