How to use Fork Join in Java 1.7 - Tutorial with Example
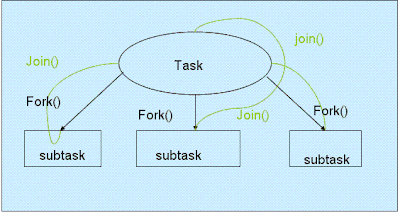
What is fork Join framework in Java: Already popular project coin of JDK7 release has presented lot of good feature e.g automatic resource management, string in switch case, better exception handling in JDK7 etc. On of other important feature to note is fork join as name implies it divide one task into several small task as a new fork means child and join all the fork when all the sub-tasks complete. Fork/join tasks is “pure” in-memory algorithms in which no I/O operations come into picture.it is based on a work-stealing algorithm. Concept of fork join would be much clear by following diagram.
How fork join comes in existence:
Java’s most attractive part is it makes things easier and easier.for doing things faster java has given us concurrency concept but dealing with concurrency is not easy because we have to deal with thread synchronization and shared data. When we have to work with small piece of code it is easy to handle synchronization and atomicity, but it becomes for complex when code base and number of threads increased, its really challenging where several threads are working together to accomplish a large task so again java has tried to make things easy and simplifies this concurrency using Executors and Thread Queue.
 When we compare Executors with old Thread it has made management of concurrent task very easy and it work on divide and conqueralgorithm and create sub-tasks and communicate with each other to complete.But The problem with the executors framework is that a Callable is free to submit a new sub-task to its executor and wait for its result in a synchronous or asynchronous fashion. The issue is that of parallelism: When a Callable waits for the result of another Callable, it is put in a waiting state, and thus wasting an opportunity to handle another Callable queued for execution.
When we compare Executors with old Thread it has made management of concurrent task very easy and it work on divide and conqueralgorithm and create sub-tasks and communicate with each other to complete.But The problem with the executors framework is that a Callable is free to submit a new sub-task to its executor and wait for its result in a synchronous or asynchronous fashion. The issue is that of parallelism: When a Callable waits for the result of another Callable, it is put in a waiting state, and thus wasting an opportunity to handle another Callable queued for execution.
To solve this issue java 7 has given the concept of parallelism.New fork-join framework has been added in java.util.concurrent package.New fork-join executor framework has been created which is responsible for creating one new task object which is again responsible for creating new sub-task object and waiting for sub-task to be completed.internally it maintains a thread pool and executor assign pending task to this thread pool to complete when one task is waiting for another task to complete. whole Idea of fork-join framework is to leverage multiple processors of advanced machine.
Fork Join framework in JDK7
How to code using fork-join framework:
Fork-join functionality is achieved by ForkjoinTask object, it has two method fork() and join () Method.
- The fork() method allows a new ForkJoinTask to be launched from an existing one.
- The join() method allows a ForkJoinTask to wait for the completion of another one.
Again ForkjoinTask object has been of two types: RecursiveAction and RecursiveTask which is more specialized form of this instance. While RecursiveAction represent executions that do not yield a return value, Instances of RecursiveTask yield return values.
I will try to add a suitable example for fork-join framework once I get some time, I am still looking for decent example which best suited fork join framework.
Some of my other tutorial in Java
How to implement Thread in Java ?Example of Runnable interface
Difference between ConcurrentHashMap and Collections.synchronizedMap and Hashtable in Java
How Synchronization works in Java, synchronized block and method
What is Abstraction in java ?
How to convert String to int in Java?
Difference between ConcurrentHashMap and Collections.synchronizedMap and Hashtable in Java
How Synchronization works in Java, synchronized block and method
What is Abstraction in java ?
How to convert String to int in Java?
No comments:
Post a Comment