JBoss CXF Web services
Page 1 of 2
Apache CXF is an open source services framework. CXF helps you build and develop services using frontend programming APIs, like JAX-WS and JAX-RS. These services can speak a variety of protocols such as SOAP, XML/HTTP, RESTful HTTP, or CORBA and work over a variety of transports such as HTTP, JMS or JBI.
Developing the Web service
Create a new Dynamic Web Project from Eclipse Menu and select Target runtime and configuration "JBoss AS 6"
If you don't have a recent version of JBoss Tools installed you will not be able to see in the JBoss Community server list JBoss AS 6. However choosing JBoss AS 5 (and pointing to JBoss AS 6 installation) will just work fine
We will add at first the Web services an interface which will be used by our implementation.
and this is the implementation class:
Now it's time to register your Web service. Add your web service in web.xml:
A JAX-WS Endpoint can be also configured using Spring XML file in addition to using the JAX-WS APIs. Once you've created your server implementation, you simply need to provide the class name and an address.
Here's a sample jbossws-cxf.xml
For more details about configuring Apache CXF web services with Apache CXF configuration file, please refer tohttp://community.jboss.org/wiki/JBossWS-StackCXFUserGuide
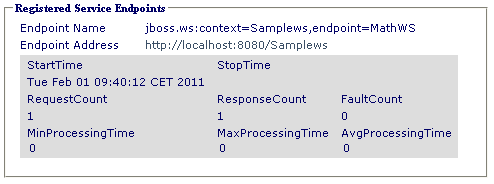
Deploy the service. If everything compiled correctly, you should see in the list of the deployed services your mathWS service.
Point the browser at http://localhost:8080/jbossws/services and check it.
Develop a CXF client.
Here's a minimal client implementation:
Notice the use of JaxWsProxyFactoryBean which is a factory for creating JAX-WS proxies. This class provides access to the internal properties used to set-up proxies. Using it provides more control than the standard JAX-WS APIs.<
No comments:
Post a Comment